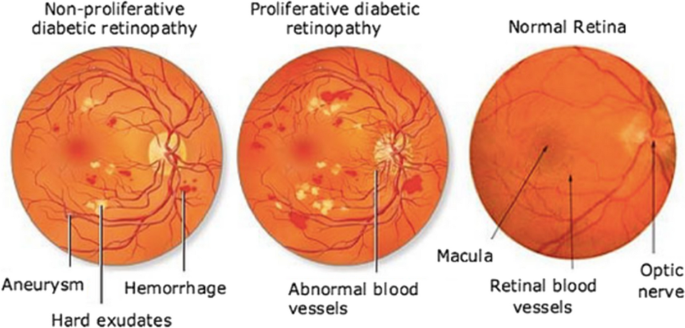
A groundbreaking study leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) has revealed new insights into retinal thickness, potentially offering an innovative way to detect Type 2 diabetes and dementia at an early stage. Scientists have created the most detailed maps of the retina ever produced, shedding light on how changes in retinal structure may serve as an early warning system for these conditions.
The study, conducted by leading ophthalmologists and AI specialists, used advanced imaging techniques to analyze subtle variations in retinal layers, which can indicate neurodegenerative and metabolic disorders. Researchers found that individuals with Type 2 diabetes and cognitive decline exhibited distinct changes in retinal thickness, suggesting that eye scans could become a non-invasive diagnostic tool for early disease detection.
By combining AI-driven image analysis with vast retinal scan datasets, the research team has unlocked a new frontier in precision medicine. The findings could revolutionize diabetes and dementia screening, enabling faster interventions and personalized treatment plans before symptoms manifest. Experts believe that integrating AI-powered retinal scans into routine eye exams could transform healthcare by detecting systemic diseases earlier than ever before.
This technology could reshape medical diagnostics to provide an easy, accessible, and cost-effective way of identifying at-risk individuals with further validation and clinical trials. Indeed, with AI pioneering areas in medical research, prediction and prevention of chronic diseases using eyes scans may be possible soon.